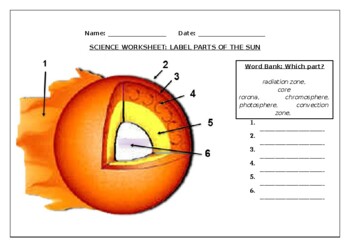
38 labeled parts of the sun
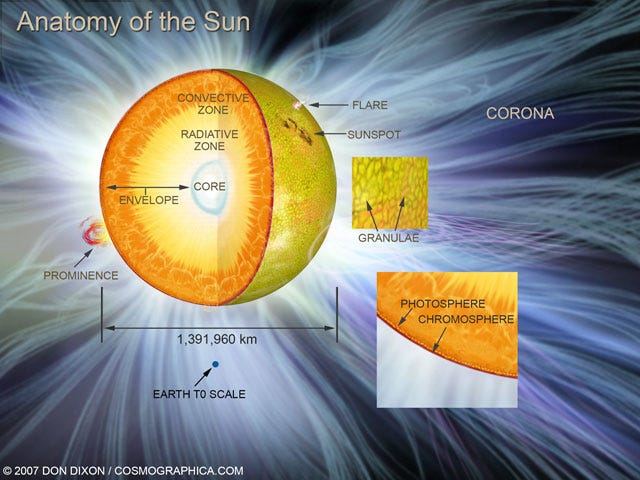
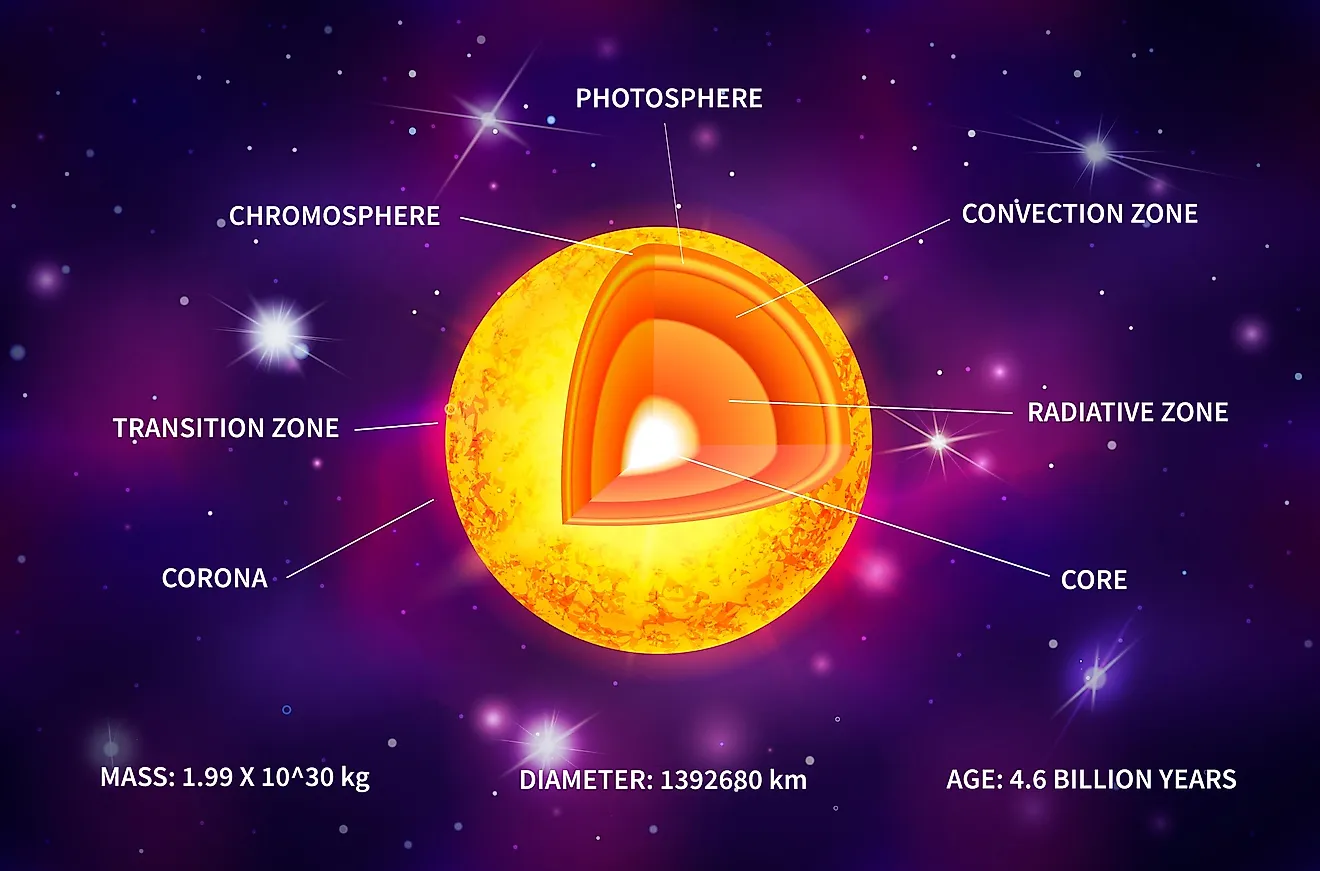
Match the labeled parts of the cell to their functions. Gives the cell ... Match the labeled parts of the cell to their functions. Gives the cell its shape: D Stores water, waste, and food: A Converts energy from the sun to chemical energy: ... The bulging middle of the cloud became the sun, and the rest of the dust and gas formed the planets, orbiting the sun in the same plane. Layers of the Sun Facts, Worksheets & The Sun For Kids - KidsKonnect The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. It is composed of seven layers: three inner layers and four outer layers. The inner layers are the core, the radiative zone and the convection zone, while the outer layers are the photosphere, the chromosphere, the transition region and the corona. See the fact file below for more information ...
Layers of the Sun | Science Facts From the Earth, the sun looks rather small. In reality, the diameter of the sun is around 860,000 miles. The Earth can fit around the sun 109 times. It is the closest star to the earth with a distance of 93 million miles. The sun is made of several complex layers, each with its own unique job that ultimately produces energy.
Labeled parts of the sun
Sun in detail: Layers & Parts of Sun. - The Last Dialogue Sun Anatomy: Parts and Layers of Sun. Sun has three main regions first is Sun's interior which further consists of three parts Core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone, the second is Sun's visible surface called photosphere, and third is Sun's atmosphere which further consists of 3 parts Chromosphere, Transition Region and Corona. What Are The Layers Of The Sun? - WorldAtlas The layers of the Sun are divided into two larger groups, the outer and the inner layers. The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. The Outer Layers Corona Transition region Chromosphere Photosphere PDF The Structure of the Sun - Space Weather Prediction Center In studying the structure of the Sun, solar physicists divide it into four domains: the interior, the surface atmospheres, the inner corona , and the outer corona. Section 1.—The Interior The Sun's interior domain includes the core, the radiative layer , and the convective layer (Figure 2-1).
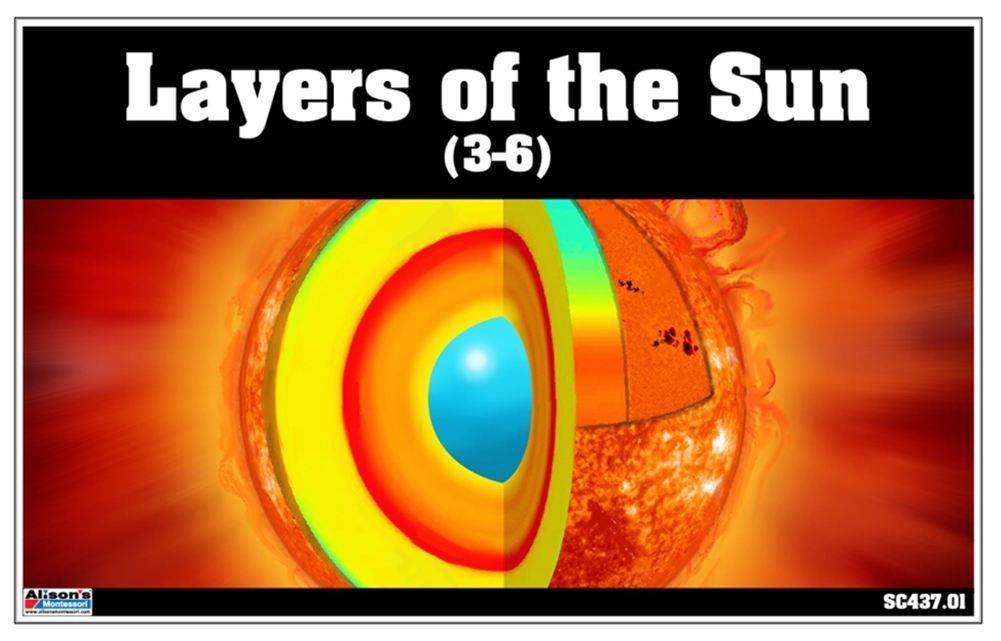
Labeled parts of the sun. 15.1 The Structure and Composition of the Sun - OpenStax The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. Some typical features in the atmosphere are shown, such as coronal holes and prominences. (credit: modification of work by NASA/Goddard) The Sun's layers are different from each other, and each plays a part in producing the energy that the Sun ultimately emits. Label Solar System Diagram Printout - EnchantedLearning.com Read the definitions, then label the diagram below. Sun - The Sun is a star at the center of our Solar System. Venus - Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is the hottest planet. Earth - Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the planet we live on. Jupiter - Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun. This gas giant is the largest planet. PDF Parts of the Sun - Montana From the center out, the layers of the sun are as follows: the solar interior which is composed of the core, the radiative zone and the convective zone. The visible surface is made up of the photosphere and the chromosphere. The outermost layer is called the corona. In this lesson, students will learn about the sun, our closest star. Guidelines 1. "Parts" of the Sun | Center for Science Education There are three main parts to the Sun's interior: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone. The core is at the center. It the hottest region, where the nuclear fusion reactions that power the Sun occur. Moving outward, next comes the radiative (or radiation) zone.
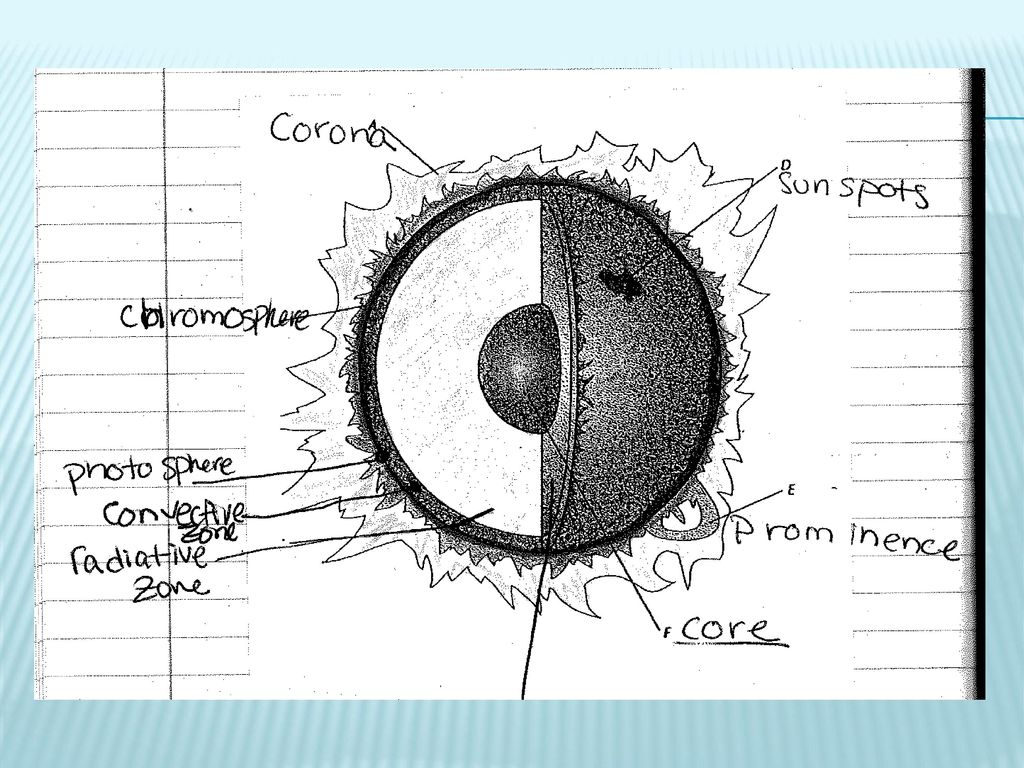
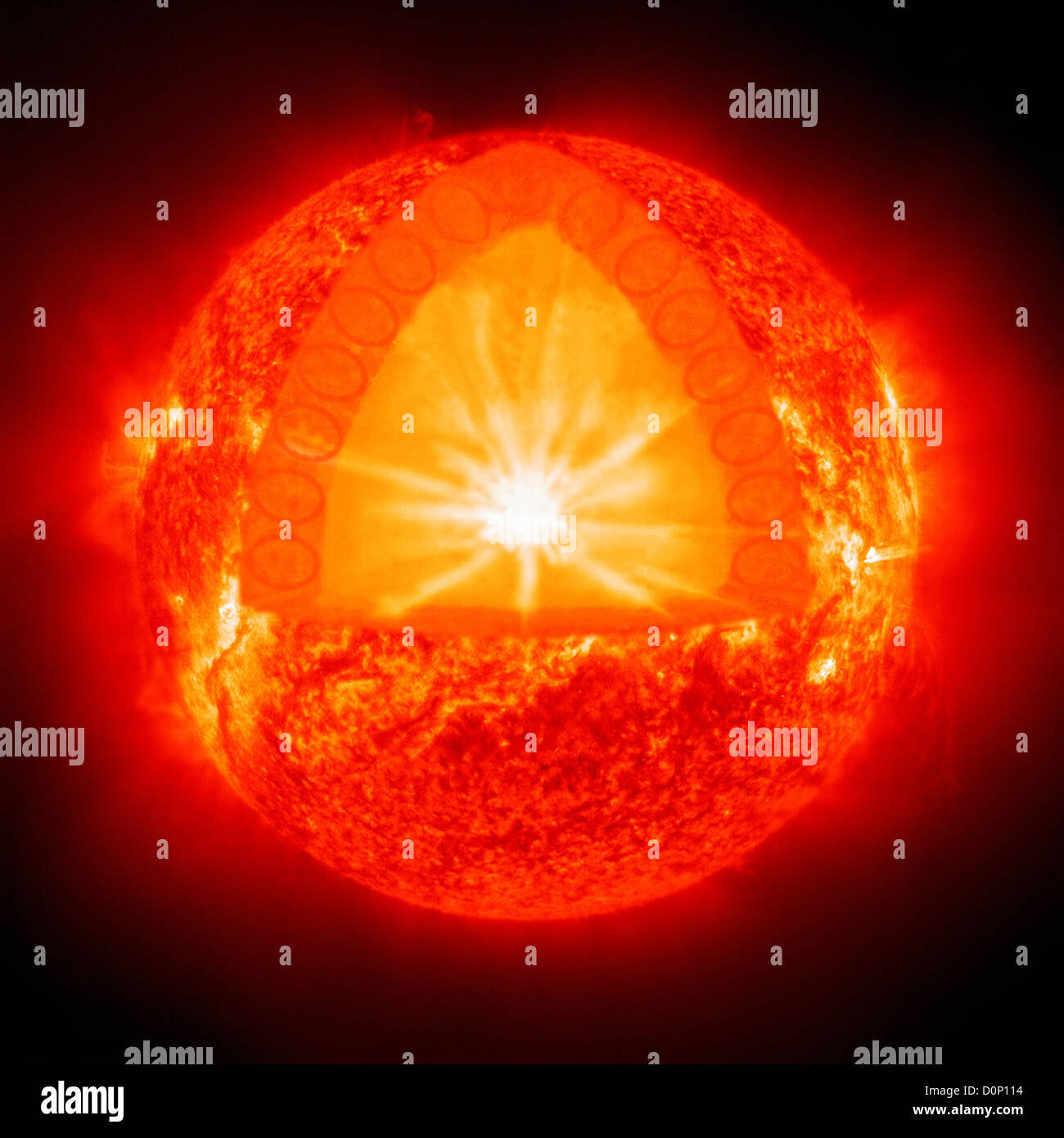
Layers of the Sun - The Sun Today with Dr. C. Alex Young The Sun, as shown by the illustration to the left, can be divided into six layers. From the center out, the layers of the Sun are as follows: the solar interior composed of the core (which occupies the innermost quarter or so of the Sun's radius),; the radiative zone, ; and the convective zone,; then there is the visible surface known as the photosphere, Anatomy of the Sun | NASA The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by magnetic field lines that restrain the electrically charged solar plasma. Occasionally larger plasma features, called prominences, form and extend far into the very tenuous and hot corona, sometimes ejecting material away from the Sun. The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A - BRAINLY Identify the parts of the Sun labeled A, B, C, D, and E. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Advertisement Answer 4.1 /5 11 368esc07 Layer A- CORE Layer B- RADIATIVE ZONE layer C- CONVECTIVE ZONE Layer D- PHOTOSPHERE Layer E- CHROMOSPHERE Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. Layer E - Corona °C re lay hai. Anti b km mm
Layers of the Sun (With Labels) - Solar System From the inside out, the solar interior consists of the core, the radiative zone, and the convection zone. The solar atmosphere is made up of the photosphere, the chromosphere, a transition region, and the corona. Beyond the corona is the solar wind, which is actually an outward flow of coronal gas. Structure of the Sun Anatomy & Diagram - Study.com There are three inner layers of the Sun. These are: The core The radiative zone The convective zone The core of the Sun is the area that extends from the center of the Sun to approximately 138,000... Sun Fact Sheet - NASA Sun Earth Ratio (Sun/Earth) Mass (10 24 kg) 1,988,500. 5.9724: 333,000. GM (x 10 6 km 3 /s 2) 132,712. 0.39860: 333,000. Volume (10 12 km 3) 1,412,000. 1.083: ... Typical magnetic field strengths for various parts of the Sun Polar Field: 1 - 2 Gauss Sunspots: 3000 Gauss Prominences: 10 - 100 Gauss Chromospheric plages: 200 Gauss Bright ... PDF The Structure of the Sun - European Space Agency The different layers of the Sun The Sun, like other stars, is a huge spherical object made of hydrogen and helium. Its diameter reaches 1.400.000 km, or 109 times the Earth's diameter; but is 4 times less dense than the Earth due to its composition. The Sun is not only made of the glowing gas that we see with a telescope. It has, exactly
The sun's atmosphere: Photosphere, chromosphere and corona The sun's photosphere is about 300 miles (500 kilometers) thick, which is relatively thin when compared with the 435,000 miles (700,000 km) radius of the sun. ... Space is part of Future US Inc ...
Parts of the SUN and definitions Diagram | Quizlet Core The central part of the earth below the mantle Sunspot A dark area of gas on the sun's surface that is cooler than surrounding gases. Photosphere The inner layer of the sun's atmosphere Prominence A large, bright feature extending outward from the Sun's surface. Chromosphere The middle layer of the sun's atmosphere YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE...
Regions and Features of the Sun | Center for Science Education The main regions of the Sun include its interior, surface (photosphere), and atmosphere. SOHO (ESA & NASA) Planets such as Earth have regions with specific traits - places like continents, oceans, and polar ice caps. The Sun also has regions, but of a very different nature.
Parts of the Sun Nomenclature from Montessori for Everyone 6 picture cards for parts of the Sun; 6 labels for parts of the Sun; 6 picture/label cards (control cards) for parts of Sun; Definitions for each part of the Sun; Instructions for making this material; Parts are: Sun, chromosphere, photosphere, convective zone, radiative zone, and core. Size: Nomenclature cards are approximately 3 x 4 in. with ...
The Sun | Earth Science | | Course Hero The mass of the Sun is 99.8% of the mass of our solar system. The Sun is mostly made of hydrogen with smaller amounts of helium in the form of plasma. The main part of the Sun has three layers: the core, radiative zone, and convection zone. The Sun's atmosphere also has three layers: the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona.
Layers of the Sun | NASA The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona. IRIS will focus its investigation on the Chromosphere and Transition Region. More detail on the outer layers follows: Photosphere - The photosphere is the deepest layer of the Sun that we can observe directly.
SUN PARTS DEFINITION Flashcards | Quizlet currents of hot gases rise and falls grandules a line or squiggle that is about 600 miles across solar wind a stream of particles that flows out from the sun corona a hallo or crown only seen in a solar eclipse 1 million miles high photoshere sphere of light 340 miles deep surface layes the part of sun we can see flares
The Sun - Imagine the Universe! The Sun contains about 92% hydrogen and 8% helium, with just a tiny bit of the other common elements we find on Earth. Compare that to Earth, where the most common elements are oxygen, magnesium, silicon, and iron. On Earth, hydrogen barely makes the top 10 list of common elements, and helium is extremely rare.
Layers of the Sun | Parts of the Sun | DK Find Out The structure of the sun is made up of four layers. At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere.
DOC Loudoun County Public Schools / Overview The inner layer of the sun's atmosphere, and also the part that we see is called the PHOTOSPHERE 13. The RADIATIVE ZONE is the thickest layer of the sun. 14. Huge fiery arms or loops extending from the sun's surface are called SOLAR PROMINENCES 15.FUSION is the combining of a lighter elements to form a heavier element. True/False 16.
PDF The Structure of the Sun - Space Weather Prediction Center In studying the structure of the Sun, solar physicists divide it into four domains: the interior, the surface atmospheres, the inner corona , and the outer corona. Section 1.—The Interior The Sun's interior domain includes the core, the radiative layer , and the convective layer (Figure 2-1).
What Are The Layers Of The Sun? - WorldAtlas The layers of the Sun are divided into two larger groups, the outer and the inner layers. The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. The Outer Layers Corona Transition region Chromosphere Photosphere
Sun in detail: Layers & Parts of Sun. - The Last Dialogue Sun Anatomy: Parts and Layers of Sun. Sun has three main regions first is Sun's interior which further consists of three parts Core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone, the second is Sun's visible surface called photosphere, and third is Sun's atmosphere which further consists of 3 parts Chromosphere, Transition Region and Corona.






















Post a Comment for "38 labeled parts of the sun"